Feature distribution statistics as a loss objective for robust white balance correction
Machine Vision and Applications
Abstract
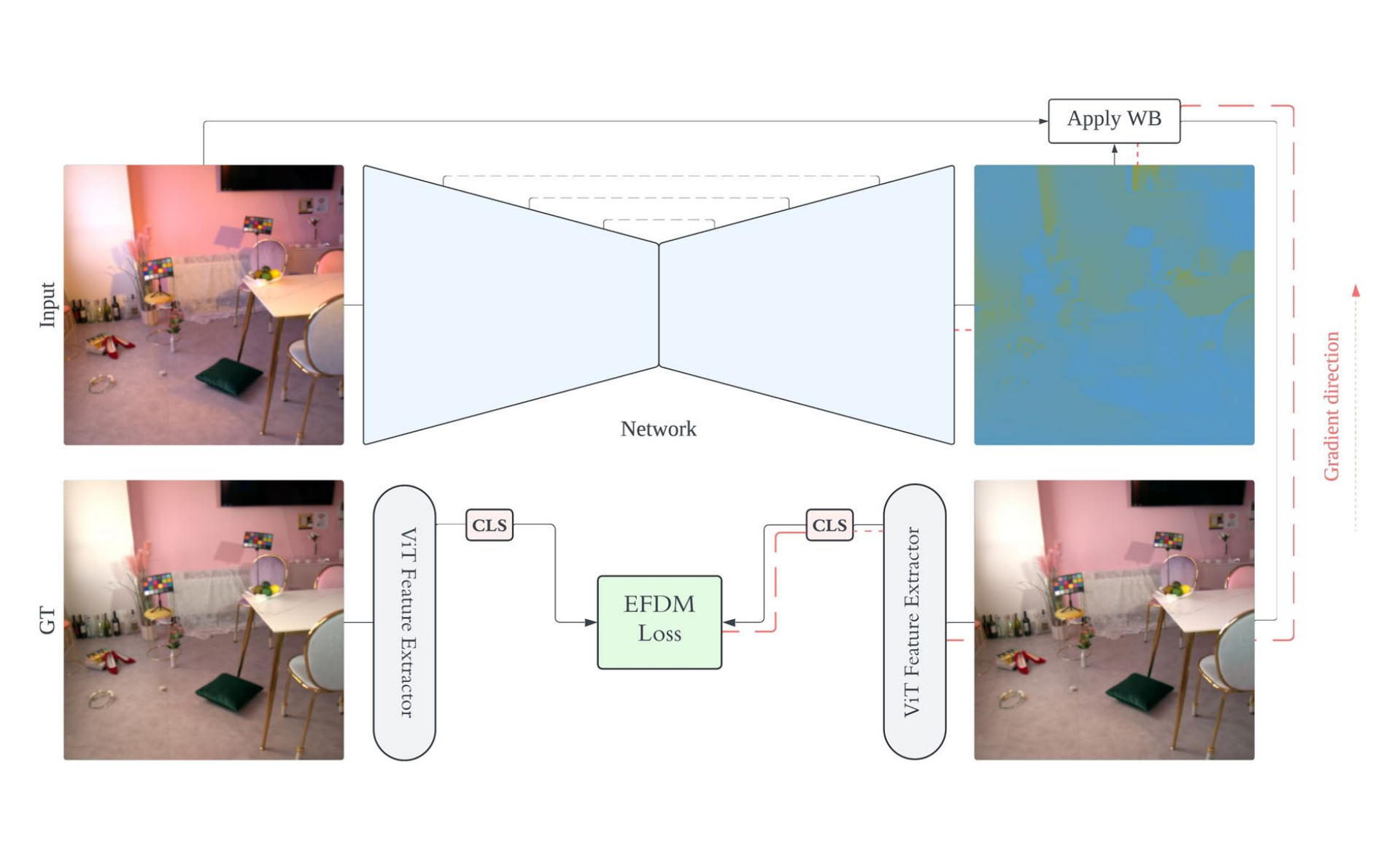
White balance (WB) correction is critical for accurate color reproduction in digital images, especially under complex, multi-illuminant lighting conditions. Traditional methods, such as the Gray-World assumption, rely on global statistics and struggle in real-world, non-uniform lighting scenarios. Modern deep learning approaches, including convolutional and attention-based architectures, have significantly advanced WB correction but often fail to explicitly account for higher-order feature distribution statistics, which may limit their robustness in challenging environments. This study introduces a novel framework that leverages Exact Feature Distribution Matching (EFDM) as a loss objective to align feature distributions across multiple moments, including mean, variance, skewness, and kurtosis. By modeling lighting as a style factor, the method explicitly addresses distributional shifts caused by complex illumination, offering a robust solution for WB correction. The framework integrates EFDM with a Vision Transformer architecture, enabling precise handling of global and local lighting variations. Extensive experiments on the large-scale multi-illuminant (LSMI) dataset demonstrate the superiority of the proposed approach over state-of-the-art methods and commonly used loss functions when applied to the same architecture. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations highlight its effectiveness in achieving perceptually accurate WB correction, particularly in multi-illuminant environments. By bridging statistical modeling with modern deep learning, this work establishes the critical role of feature distribution alignment in advancing WB correction and sets a new benchmark for robustness and generalization in complex lighting scenarios.
Bibtex:
@article{kinli2025feature,
title={Feature distribution statistics as a loss objective for robust white balance correction},
author={K{\i}nl{\i}, Furkan and K{\i}ra{\c{c}}, Furkan},
journal={Machine Vision and Applications},
volume={36},
number={3},
pages={1--20},
year={2025},
publisher={Springer}
}
