Advancing white balance correction through deep feature statistics and feature distribution matching
Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation
Abstract
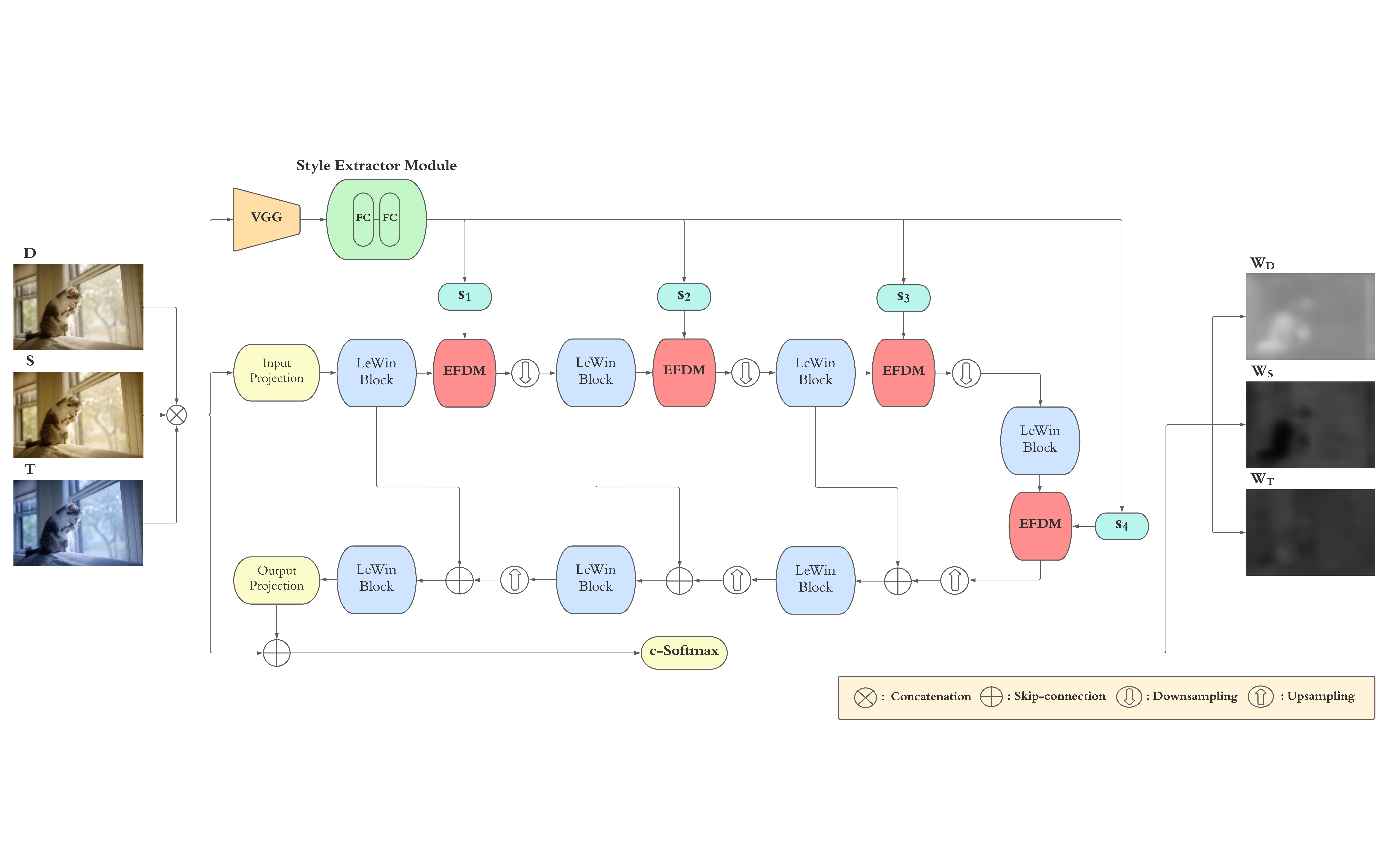
Auto-white balance (AWB) correction is a crucial process in digital imaging, ensuring accurate and consistent color correction across varying lighting conditions. This study presents an innovative AWB correction method that conceptualizes lighting conditions as the style factor, allowing for more adaptable and precise color correction. Previous studies predominantly relied on Gaussian distribution assumptions for feature distribution alignment, which can limit the ability to fully exploit the style information as a modifying factor. To address this limitation, we propose a U-shaped Transformer-based architecture, where the learning objective of style factor enforces matching deep feature statistics using the Exact Feature Distribution Matching algorithm. Our proposed method consistently outperforms existing AWB correction techniques, as evidenced by both extensive quantitative and qualitative analyses conducted on the Cube+ and a synthetic mixed-illuminant dataset. Furthermore, a systematic component-wise analysis provides deeper insights into the contributions of each element, further validating the robustness of the proposed approach.
Bibtex:
@article{KINLI2025104412,
title = {Advancing white balance correction through deep feature statistics and feature distribution matching},
journal = {Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation},
volume = {108},
pages = {104412},
year = {2025},
issn = {1047-3203},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2025.104412},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1047320325000264},
author = {Furkan Kınlı and Barış Özcan and Furkan Kıraç},
keywords = {Auto-white balance correction, Color correction, Style transfer, Feature distribution matching, Style factor}
}
